Anal vein thrombosis
Sudden swelling of the anus with pain and a feeling of pressure after exercise or prolonged sitting.
| Anal vein thrombosis OP Check |
| Normally no indication for surgery! |
| Operation time: 5-10 Minutes |
| Hospitalization: No |
| Open wound healing: Yes |
| Inability to work: 0-7 days |
|
General anesthesia: No |
|
Costs: The costs are covered by the insurance companies. |
What is anal vein thrombosis?
Anal vein thrombosis is a sudden swelling of the anus and can be very painful. It is a small blood clot in veins that run under the skin in the anal area.
Other names are “anal thrombosis, perianal thrombosis or perianal venous thrombosis”. The term “external hemorrhoid” is often incorrectly used, but this is not anatomically correct, as hemorrhoids are located in the anal canal and not on the outside of the anus.
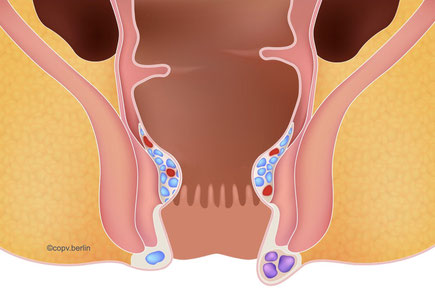
Anal vein thrombosis is an acute vascular occlusion in the anus that occurs suddenly.
The clotted blood causes a typical bluish-purple swelling, which can cause pain due to the taut skin.
Due to its external location at the edge of the anus, the thrombosis can be easily felt, in contrast to internal hemorrhoids.
“The sudden painful swelling at the edge of the anus is typical of anal vein thrombosis”
How do anal vein thromboses develop?
Many factors can trigger anal thrombosis. In some cases, however, no cause can be found. The most common triggers of anal thrombosis include thermal influences such as cold (sitting on cold surfaces), hot and humid weather, unusual physical exertion such as jogging, cycling or moving house.
Strong pushing, such as during a hard bowel movement or childbirth, can also lead to thrombosis, as can proctological procedures and anal intercourse. Hormonal factors (menstruation), alcohol and spices can also play a role in the development.
Enlarged hemorrhoidal cushions, which lead to a slowing of the flow in the veins, may promote the development of thrombosis. Enlarged haemorrhoids should therefore always be ruled out by an experienced proctologist.
What is the distribution in the population?
As anal thromboses are generally not operated on and resolve on their own, no exact figures are available. In middle adulthood, 5% of proctologic patients have anal vein thrombosis, with women and men being affected equally often. In contrast to hemorrhoidal disease, anal vein thrombosis can also occur more frequently in adolescents.
What are the symptoms of anal thrombosis?
Patients usually complain of acute onset of pain in conjunction with swelling at the edge of the anus. This may be accompanied by itching, stinging, burning and a strong feeling of pressure. In contrast, there is no blood in a fresh anal thrombosis.
The diagnosis is made by the proctologist. On examination, a bulging to coarse, bluish-red swelling the size of a pea to a plum can usually be seen at the edge of the anus.
Occasionally, several small thrombi can also be felt. If the thrombi are visible, the diagnosis has been made. Further examinations are not necessary. Anal thrombosis cannot be pushed into the anus as it comes from the outside. Hemorrhoids, on the other hand, can be pushed back with a finger, as they also come from the inside.
“Anal thrombosis cannot be pushed into the anus because it comes from the outside - unlike hemorrhoids, which come from the inside”
How is anal thrombosis treated?
Anal vein thrombosis does not require surgery, as the blood clot dissolves completely. Therefore, only pain-relieving measures such as ointments and gels with lidocaine and anti-inflammatory painkillers such as ibuprofen or diclofenac are required.
Thrombus-dissolving ointments have no effect on the course of the disease. The pain usually subsides significantly after 2-5 days. The tension decreases as the skin becomes softer again (regression of the edema). Depending on its size, the blood clot can take up to 6 weeks to break down, but there is no more pain.
In the case of very large thromboses, the skin may burst due to the strong pressure and bleeding with black crumbs may occur, which corresponds to the clotted blood. This provides sudden relief. The wound then only needs to be dabbed out with water twice a day and heals without any problems.
It is important to note that anal thrombosis is a small blockage of a blood vessel and that this blood clot (thrombus) cannot travel any further, i.e. it cannot lead to an embolism! Most people have had an anal vein thrombosis in their lives, so it is a very common phenomenon.
When does surgery have to be performed and how?
Surgery may be necessary for very large and painful anal vein thromboses. The same applies to frequently recurring thromboses, e.g. at monthly intervals. The thrombus should always be completely excised and not just incised, which is not very effective. This can be done under local anesthesia with electricity. The wound is not sutured and remains open. There is no risk of infection if the wound is regularly washed out in the first 2 weeks.
Prophylaxis
There is no way to prevent anal vein thrombosis. An existing hemorrhoidal disease should be treated by a proctologist in the event of recurrent anal thrombosis.
You are welcome to book an appointment with our doctors.
We look forward to hearing from you.

